貨號
產品規格
售價
備注
BN40864R-100ul
100ul
¥2470.00
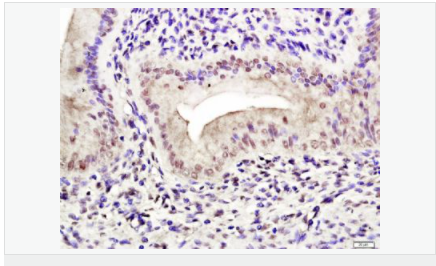
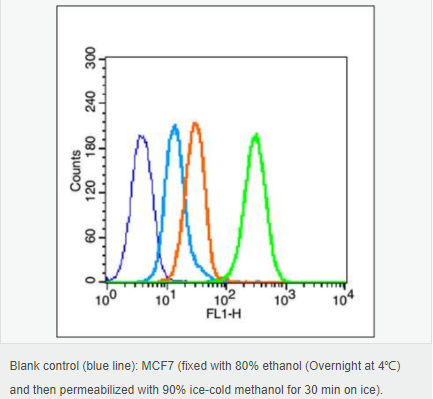
交叉反應:Human,Rat(predicted:Mouse,Pig,Rabbit) 推薦應用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
產品描述
| 英文名稱 | Phospho-Estrogen Receptor alpha (Ser118) |
| 中文名稱 | 磷酸化雌激素受體α抗體 |
| 別 名 | Estrogen Receptor alpha (phospho S118); p-Estrogen Receptor alpha (phospho S118); ER (phospho S118); p-ER (phospho S118); ER alpha (Phospho-Ser118); ER alpha (Phospho-S118); Phospho-ER alpha (S118); ; Phospho-ER alpha (Ser118); p-ER alpha (Ser118); p-ER alpha (S118); Phospho-Estrogen Receptor alpha (S118); Phospho-Estrogen Receptor alpha (S118); Estradiol receptor; Estrogen receptor alpha; Estradiol Receptor-alpha; Estrogen Receptor 1; Atherosclerosis, susceptibility to, included; DKFZp686N23123; ER Alpha; ER; ER-alpha; ERalpha; ER[a]; Era; ESR; ESR1; ESR1_HUMAN; ESR2; ESRA; Estr; Estrogen receptor 1 (alpha); Estrogen resistance, included; HDL cholesterol, augmented response of, to hormone replacement, included; Myocardial infarction, susceptibility to, included; NR3A1; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 1; OTTHUMP00000017718; OTTHUMP00000017719; RNESTROR. |
| 產品類型 | 磷酸化抗體 |
| 研究領域 | 腫瘤 免疫學 染色質和核信號 神經生物學 信號轉導 表觀遺傳學 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應 | Human, Rat, (predicted: Mouse, Pig, Rabbit, ) |
| 產品應用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 Flow-Cyt=1μg /Test IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 66kDa |
| 細胞定位 | 細胞核 細胞漿 細胞膜 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated Synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human ER alpha around the phosphorylation site of Ser118:QL(p-S)PF |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產品介紹 | Estrogen and progesterone receptor are members of a family of transcription factors that are regulated by the binding of their cognate ligands. The interaction of hormone-bound estrogen receptors with estrogen responsive elements(EREs) alters transcription of ERE-containing genes. The carboxy terminal region of the estrgen receptor contains the ligand binding domain, the amino terminus serves as the transactivation domain, and the DNA binding domain is centrally located. Two forms of estrogen receptor have been identified, ER alpha and ER beta. ER alpha and ER beta have been shown to be differentially activated by various ligands. The biological response to progesterone is mediated by two distinct forms of the human progesterone receptor (hPR-A and hPR-B), which arise from alternative splicing. In most cells, hPR-B functions as a transcriptional activator of progesterone-responsive gene, whereas hPR-A function as a transcriptional inhibitor of all steroid hormone receptors. Function: Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1. Subunit: Binds DNA as a homodimer. Can form a heterodimer with ESR2. Isoform 3 can probably homodimerize or heterodimerize with isoform 1 and ESR2. Interacts with FOXC2, MAP1S, SLC30A9, UBE1C and NCOA3 coactivator. Interacts with EP300; the interaction is estrogen-dependent and enhanced by CITED1. Interacts with CITED1; the interaction is estrogen-dependent. Interacts with NCOA5 and NCOA6 coactivators. Interacts with NCOA7; the interaction is a ligand-inducible. Interacts with PHB2, PELP1 and UBE1C. Interacts with AKAP13. Interacts with CUEDC2. Interacts with KDM5A. Interacts with SMARD1. Interacts with HEXIM1. Interacts with PBXIP1. Interaction with MUC1 is stimulated by 7 beta-estradiol (E2) and enhances ERS1-mediated transcription. Interacts with DNTTIP2, FAM120B and UIMC1. Interacts with isoform 4 of TXNRD1. Interacts with MLL2. Interacts with ATAD2 and this interaction is enhanced by estradiol. Interacts with KIF18A and LDB1. Interacts with RLIM (via C-terminus). Interacts with MACROD1. Interacts with SH2D4A and PLCG. Interaction with SH2D4A blocks binding to PLCG and inhibits estrogen-induced cell proliferation. Interacts with DYNLL1. Interacts with CCDC62 in the presence of estradiol/E2; this interaction seems to enhance the transcription of target genes. Interacts with NR2C1; the interaction prevents homodimerization of ESR1 and suppresses its transcriptional activity and cell growth. Interacts with DYX1C1. Interacts with PRMT2. Interacts with PI3KR1 or PI3KR2, SRC and PTK2/FAK1. Interacts with RBFOX2. Interacts with STK3/MST2 only in the presence of SAV1 and vice-versa. Binds to CSNK1D. Interacts with NCOA2; NCOA2 can interact with ESE1 AF-1 and AF-2 domains simultaneously and mediate their transcriptional synergy. Interacts with DDX5. Interacts with NCOA1; the interaction seems to require a self-association of N-terminal and C-terminal regions. Interacts with ZNF366, DDX17, NFKB1, RELA, SP1 and SP3. Interacts with NRIP1. Subcellular Location: Isoform 1: Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Note=A minor fraction is associated with the inner membrane. Isoform 3: Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=Associated with the inner membrane via palmitoylation (Probable). At least a subset exists as a transmembrane protein with a N-terminal extracellular domain. Nucleus. Golgi apparatus. Cell membrane. Note=Colocalizes with ZDHHC7 and ZDHHC21 in the Golgi apparatus where most probably palmitoylation occurs. Associated with the plasma membrane when palmitoylated. Tissue Specificity: Widely expressed. Isoform 3 is not expressed in the pituitary gland. Post-translational modifications: Phosphorylated by cyclin A/CDK2 and CK1. Phosphorylation probably enhances transcriptional activity. Self-association induces phosphorylation. Glycosylated; contains N-acetylglucosamine, probably O-linked. Ubiquitinated. Deubiquitinated by OTUB1. Dimethylated by PRMT1 at Arg-260. The methylation may favor cytoplasmic localization. Palmitoylated (isoform 3). Not biotinylated (isoform 3). Palmitoylated by ZDHHC7 and ZDHHC21. Palmitoylation is required for plasma membrane targeting and for rapid intracellular signaling via ERK and AKT kinases and cAMP generation, but not for signaling mediated by the nuclear hormone receptor. Similarity: Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR3 subfamily. Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain. SWISS: P03372 Gene ID: 2099 Database links: Entrez Gene: 2099 Human Entrez Gene: 13982 Mouse Omim: 133430 Human SwissProt: P03372 Human SwissProt: P19785 Mouse Unigene: 208124 Human Unigene: 463262 Mouse Unigene: 9213 Mouse Unigene: 10595 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |