貨號(hào)
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價(jià)
備注
BN41463R-50ul
50ul
¥1486.00
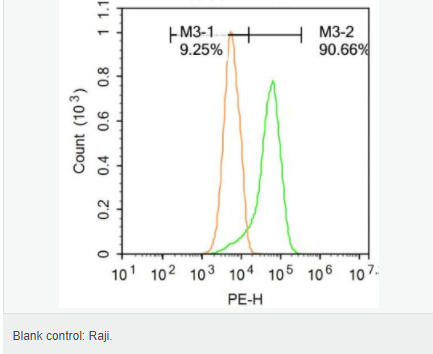
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Rabbit) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41463R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Rabbit) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41463R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Rabbit) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
產(chǎn)品描述
| 英文名稱 | presenilin 1 |
| 中文名稱 | 早老素蛋白-1抗體 |
| 別 名 | Presenilin-1 NTF subunit; AD 3; AD3; Ad3h; Alzheimer Disease 3; EC 3.4.23.; FAD; Homo Sapiens Clone CC44 Senilin 1; Presenilin 1 Alzheimer disease 3; Presenilin 1; Presenilin1; Protein S182; PS 1; PS-1; PS1; PSEN 1; PSEN1; PSN 1; PSN1; PSN1_HUMAN; PSNL 1; PSNL1; S182; S182 Protein; Senilin 1; Senilin1. |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 神經(jīng)生物學(xué) 細(xì)胞凋亡 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Human, Rat, (predicted: Mouse, Dog, Pig, Cow, Rabbit, ) |
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 Flow-Cyt=1ug/test IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復(fù)) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
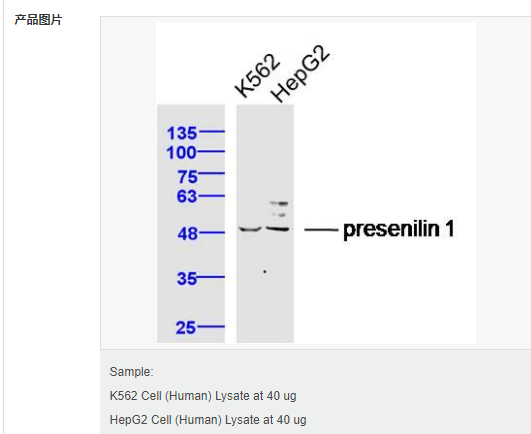
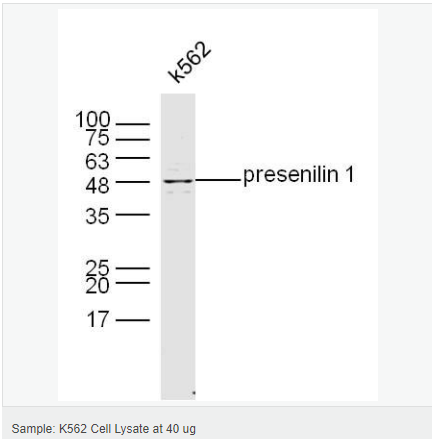
| 分 子 量 | 34/52kDa |
| 細(xì)胞定位 | 細(xì)胞漿 細(xì)胞膜 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Presenilin-1 NTF subunit:10-80/467 |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲(chǔ) 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients with an inherited form of the disease carry mutations in the presenilin proteins (PSEN1; PSEN2) or in the amyloid precursor protein (APP). These disease-linked mutations result in increased production of the longer form of amyloid-beta (main component of amyloid deposits found in AD brains). Presenilins are postulated to regulate APP processing through their effects on gamma-secretase, an enzyme that cleaves APP. Also, it is thought that the presenilins are involved in the cleavage of the Notch receptor, such that they either directly regulate gamma-secretase activity or themselves are protease enzymes. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene, the full-length nature of only some have been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008] Function: Probable catalytic subunit of the gamma-secretase complex, an endoprotease complex that catalyzes the intramembrane cleavage of integral membrane proteins such as Notch receptors and APP (beta-amyloid precursor protein). Requires the other members of the gamma-secretase complex to have a protease activity. May play a role in intracellular signaling and gene expression or in linking chromatin to the nuclear membrane. Stimulates cell-cell adhesion though its association with the E-cadherin/catenin complex. Under conditions of apoptosis or calcium influx, cleaves E-cadherin promoting the disassembly of the E-cadherin/catenin complex and increasing the pool of cytoplasmic beta-catenin, thus negatively regulating Wnt signaling. May also play a role in hematopoiesis. Subunit: Homodimer. Component of the gamma-secretase complex, a complex composed of a presenilin homodimer (PSEN1 or PSEN2), nicastrin (NCSTN), APH1 (APH1A or APH1B) and PEN2. Such minimal complex is sufficient for secretase activity. Other components which are associated with the complex include SLC25A64, SLC5A7, PHB and PSEN1 isoform 3. Predominantly heterodimer of a N-terminal (NTF) and a C-terminal (CTF) endoproteolytical fragment. Associates with proteolytic processed C-terminal fragments C83 and C99 of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Associates with NOTCH1. Associates with cadherin/catenin adhesion complexes through direct binding to CDH1 or CDH2. Interaction with CDH1 stabilizes the complex and stimulates cell-cell aggregation. Interaction with CDH2 is essential for trafficking of CDH2 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane. Interacts with CTNND2, CTNNB1, HERPUD1, FLNA, FLNB, MTCH1, PKP4 and PARL. Interacts through its N-terminus with isoform 3 of GFAP. Interacts with DOCK3. Subcellular Location: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Golgi apparatus membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell surface. Note=Bound to NOTCH1 also at the cell surface. Colocalizes with CDH1/2 at sites of cell-cell contact. Colocalizes with CTNNB1 in the endoplasmic reticulum and the proximity of the plasma membrane. Also present in azurophil granules of neutrophils. Tissue Specificity: Expressed in a wide range of tissues including various regions of the brain, liver, spleen and lymph nodes. Post-translational modifications: Heterogeneous proteolytic processing generates N-terminal (NTF) and C-terminal (CTF) fragments of approximately 35 and 20 kDa, respectively. During apoptosis, the C-terminal fragment (CTF) is further cleaved by caspase-3 to produce the fragment, PS1-CTF12. After endoproteolysis, the C-terminal fragment (CTF) is phosphorylated on serine residues by PKA and/or PKC. Phosphorylation on Ser-346 inhibits endoproteolysis. DISEASE: Defects in PSEN1 are a cause of Alzheimer disease type 3 (AD3) [MIM:607822]. AD3 is a familial early-onset form of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive dementia, loss of cognitive abilities, and deposition of fibrillar amyloid proteins as intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles, extracellular amyloid plaques and vascular amyloid deposits. The major constituent of these plaques is the neurotoxic amyloid-beta-APP 40-42 peptide (s), derived proteolytically from the transmembrane precursor protein APP by sequential secretase processing. The cytotoxic C-terminal fragments (CTFs) and the caspase-cleaved products such as C31 derived from APP, are also implicated in neuronal death. Defects in PSEN1 are a cause of frontotemporal dementia (FTD) [MIM:600274]. Similarity: Belongs to the peptidase A22A family. SWISS: P49768 Gene ID: 5663 Database links: Entrez Gene: 5663 Human Entrez Gene: 19164 Mouse Omim: 104311 Human SwissProt: P49768 Human SwissProt: P49769 Mouse Unigene: 3260 Human Unigene: 998 Mouse Unigene: 44440 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. 此抗體識(shí)別分子量為45-50kDa早老素蛋白-1。PS-1主要在神經(jīng)細(xì)胞中表達(dá),早老蛋白集中于體細(xì)胞和樹突狀細(xì)胞中。相反,再早發(fā)家族AD(FAD)中和散發(fā)AD病人中,PS1免疫反應(yīng)出現(xiàn)在老年斑和神經(jīng)纖維纏結(jié)的神經(jīng)炎中。 |